Mölnlycke® Positioning Solutions
Continuous head-to-heel protection for reduced Pressure Injury risk and therapeutic positioning
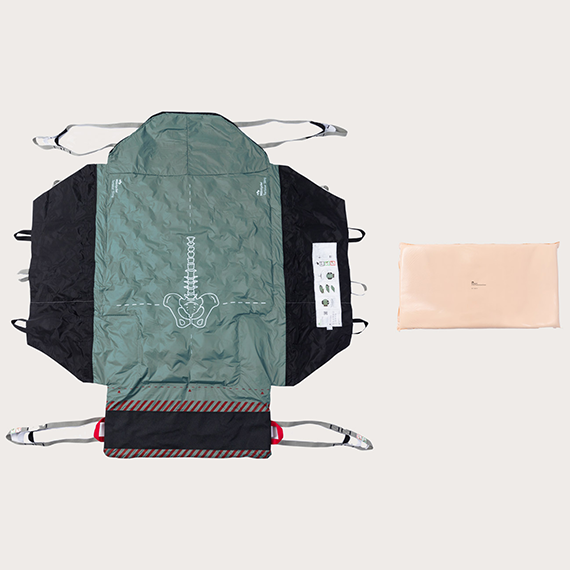
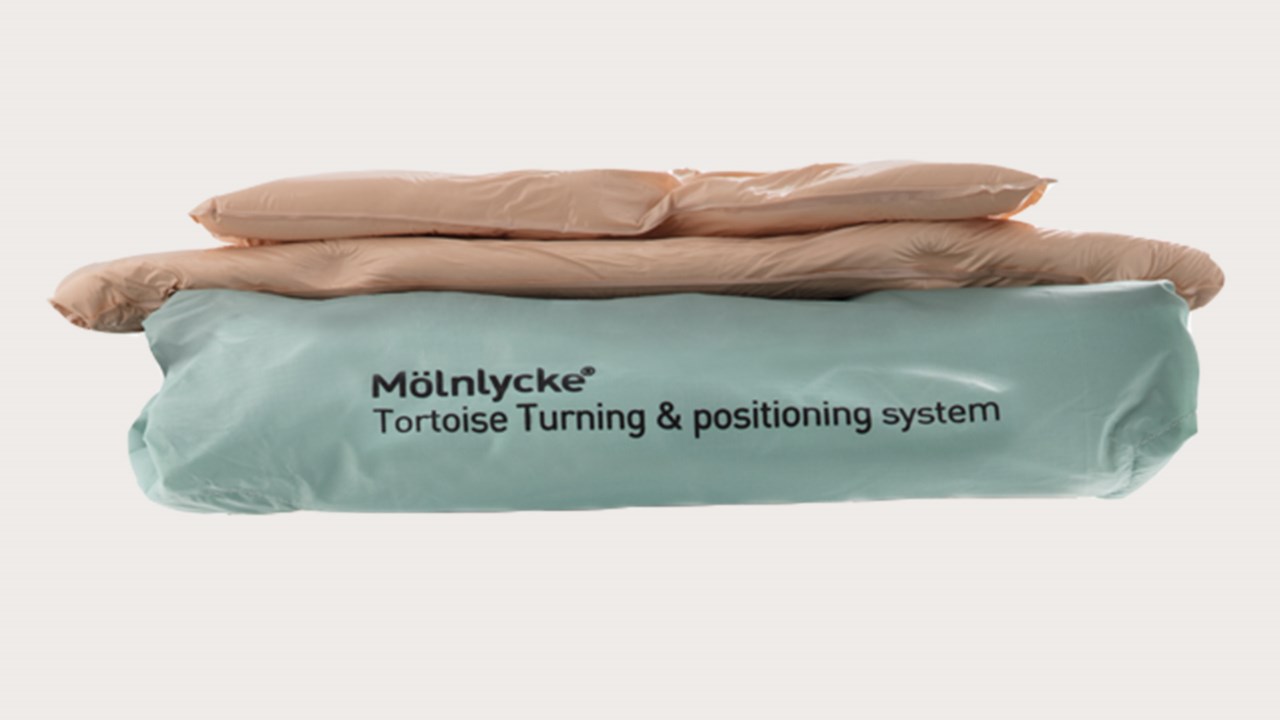
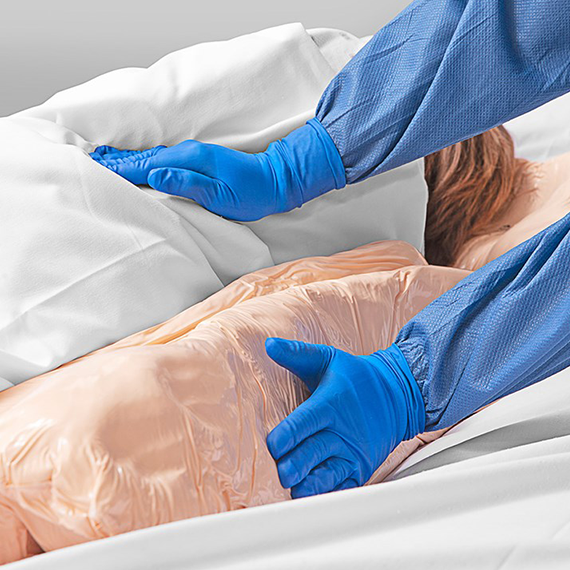
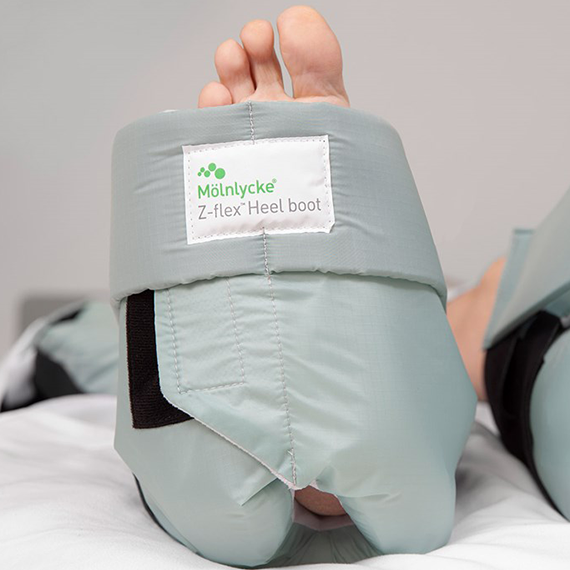
Patient positioning and device rotation are two of the five nursing interventions for pediatric pressure injuries identified by the Children’s Hospital Alliance. The wide range of Mölnlycke's positioning systems makes them a versatile tool for patient positioning as well as offloading medical devices.
Z-FLO FLUIDIZED POSITIONERS
Easily-customizable fluidized pressure redistribution devices to assist in positioning and repositioning patients